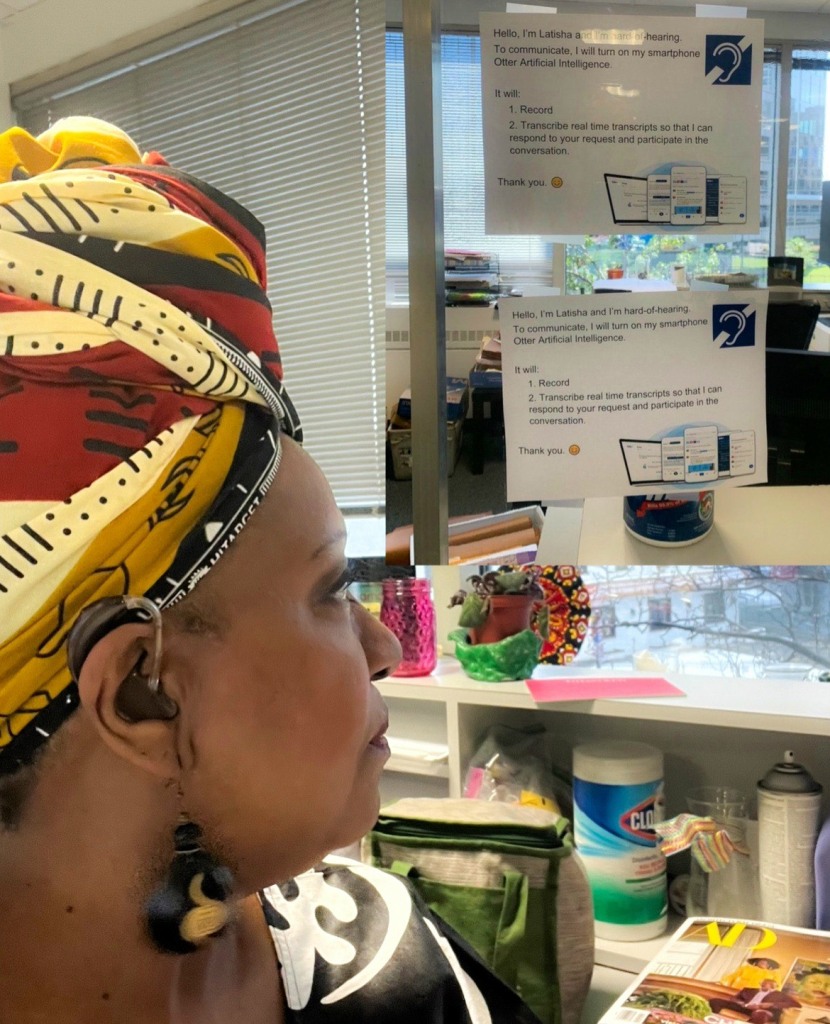
— Dr. Latisha Porter-Vaughn
As I have not yet advanced in my career despite completing my Ph.D., I continue to seek opportunities for career development. For most people, including deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals, a college degree increases their employment opportunities, economic benefits, and success in the workplace. However, disabled folks are persistently underemployed, meaning that their skills are not being used in the workplace. I have worked for the same academic institution for 32 years with most of my work in secretarial support, even though I have applied for administrative positions that would better match my education credentials. My lack of advancement in the workplace can be attributed to several factors, including a lack of disability awareness, inadequate accommodations, and non-inclusive behavior. COVID-19 provided administrators with a better understanding of the types of accommodations that can improve work performance and enable professional growth for employees with hearing loss.
Let’s begin at the beginning. In 1986, after graduating from high school, I moved from Hamilton, Ohio, to live with my sister in New Jersey. However, my life experienced a turning point. Although, I was not diagnosed with hearing loss as a newborn, only a few days after living with my big sister, she noticed something was wrong with my hearing. The big sister did what any big sister would and had my hearing checked. I learned that my entire life, I have been reading lips to understand conversations due to sensorineural hearing loss.
How was my life before the hearing loss diagnosis?
Attending college has always been my dream to enable me to climb the corporate ladder to the boardroom. I struggled academically from the 4th grade until high school, so I hesitated to take college preparatory courses. I needed help to excel despite studying and completing my homework. When I took English tests, I misspelled words and needed support. During the lecture, I needed help understanding math concepts. Hence, instead of prepping for college, I pursued vocational education to acquire office skills, such as typing and stenography, which were in demand at the time. Shorthand could have been more efficient, while typing and stenography were fast. My stenography assignments and tests were always incomplete, and I earned low grades, negatively affecting my attitude toward my teacher. I understand now that the teacher was not at fault. Because I was unaware of my hearing loss, I didn’t know I needed accommodations. Despite facing academic challenges, I remained persistent, kept believing in my dream, and received my Bachelor of Science in Business Administration in 2008.
Was 1990 the right time for accommodations?
The 20th century saw some laws aimed at improving accessibility to employment for Americans with disabilities. On July 26, 1990, the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) became law. As a civil rights law, the ADA prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities in all areas of public life, such as jobs, schools, transportation, etc. (Americans with Disabilities Act, 1990). What does this mean for me? In the workplace, employers must provide reasonable accommodations for an employee with hearing loss to perform well on the job. But access also requires administrators to understand disability awareness. Raising awareness fosters an open communication environment and enhances the interpersonal support required to succeed in the workplace with hearing loss. Employers with solid disability awareness recognize that the first attempt at accommodation might not be the best and that you must refine and adjust to various situations. An employer can demonstrate hearing loss awareness by creating a welcoming environment, knowing an employee’s specific hearing limitations, fostering an open communication environment, and having some understanding about the situational nature of accommodations.
Several months later, I applied for a position as a law school secretary. The opportunity to enter higher education was exciting. While I was proud of my 85-wpm typing speed, I knew shorthand would be challenging. When the academic Dean interviewed me, her communication skills were excellent, and she displayed courtesy, competence, and engagement. While I didn’t know this at the time, I needed these attributes in a supervisor who could create an accessible work environment. I disclosed my hearing loss to the Dean, who assured me that it would not be an issue and that the administration would provide the necessary accommodations for me to succeed at work. It sounded great, as I believed it would work. According to the Dean, employers must provide reasonable accommodations under the ADA. What are accommodations? I assumed that if the sound were loud, I would hear it, but that’s not the case – it’s more complex than that. Although I can listen to speech sounds, I can only sometimes understand some words. (See previous TMH post by Sarah Sparks about hearing versus understanding).
I accepted the job offer. My responsibilities included working with eight faculty members, answering calls, taking messages, and handling correspondence. I sat in a noisy area, and my employer, and I, in our limited knowledge of options at the time, believed that an amplified phone was the ideal accommodation. Although the telephone amplifier made louder sounds, the speech was unclear, and the voices sounded muffled. I advocated to my supervisor about my difficulty understanding speech over the telephone, yet I continued answering the phone for fifteen years. Unfortunately, I received negative performance reviews every year. I realize now that it was not appropriate for me to answer the phone during that time. It is beneficial to have a knowledgeable accommodations office on campus to provide disability support to law school students, faculty, administrators, and staff. That office might have told my supervisor and I about alternative strategies for my work accommodation.

Knowing Your Needs
Although the employee must be able to request appropriate accommodations needed to perform well on the job, the success of disabled employees also requires administrators to understand disability awareness and to establish an open communication environment. These conditions enhance the interpersonal support required to succeed in the workplace with hearing loss. Employers with solid disability awareness recognize that the first attempt at accommodation might not be the best and that you must refine and adjust to various situations. An employer can demonstrate hearing loss awareness by 1) creating a welcoming and inclusive environment with open communication, 2) knowing the communication styles and models that work best for specific employees, and 3) having some understanding about accommodations. There are soft and hard accommodations.
Soft accommodations are:
- Face the person when speaking.
- Talk in a normal tone.
- Ample-lit room.
- Talk in quiet spaces.
- Send the person an email of the time you’ll stop by their desk so they will be aware.
- Share an agenda before the meeting, so the employee knows what will be discussed.
- Understand that the employee may experience listening fatigue and need to take breaks during the meeting.
- Know that the employee can only follow one conversation at a time.
Hard Accommodations include.
- Closed captioning.
- CART or live captioning.
I refused to give up on my career and persisted through driven strategies of self-accommodation, self-management, and self-advocacy.

Latisha Porter-Vaughn is a doctoral graduate from The University of Arizona. Her Ph.D. published research is “Perceptions of Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing College Students’ Work Readiness and Preparation.” She is a research associate with the National Deaf Center on Postsecondary Outcomes to continue contributing to literature that will help improve education and employment outcomes for students who are deaf or have hearing loss. And a paralegal at Seton Hall University Center for Social Justice. She is a Gallaudet University Peer Mentor for people who have hearing loss. She is also the president of the HLAA New Jersey State Association and chair of its Scholarship Committee. She is the co-founder of the HLAA Essex Chapter and a Deaf Snapshop Mentor of SPAN New Jersey. She has self-published her book “Sounds of the Heart: The Story of a HearStrong Champion Persisting Against All Odds” and is soon to self-publish her second book “How We Hear: A Useful Guide for the Hearing to Understand Hearing Loss—Answers to 10 Questions for the Workplace & Social Situations.”